PROJECT
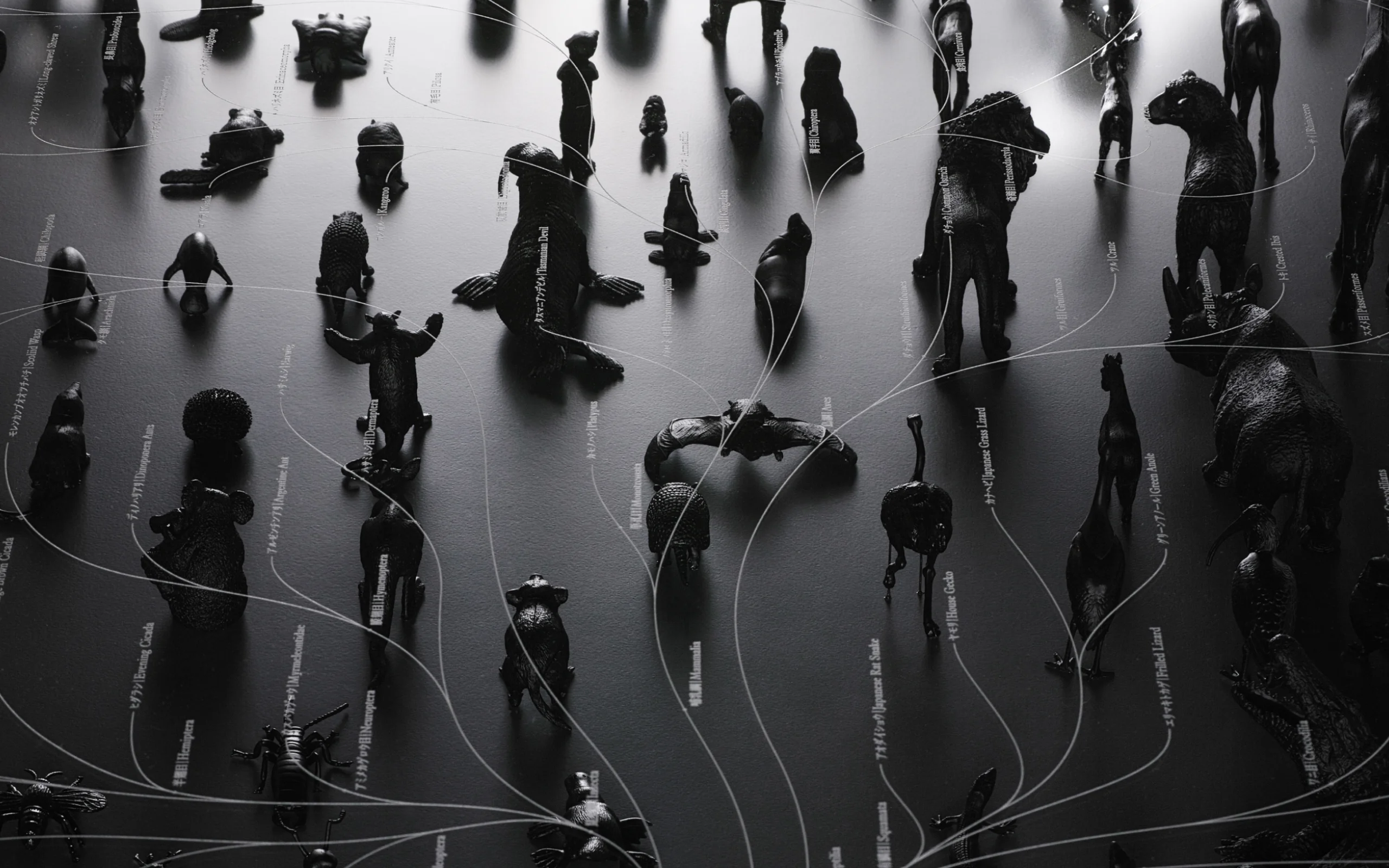
ggg/ Evolutionary Tree
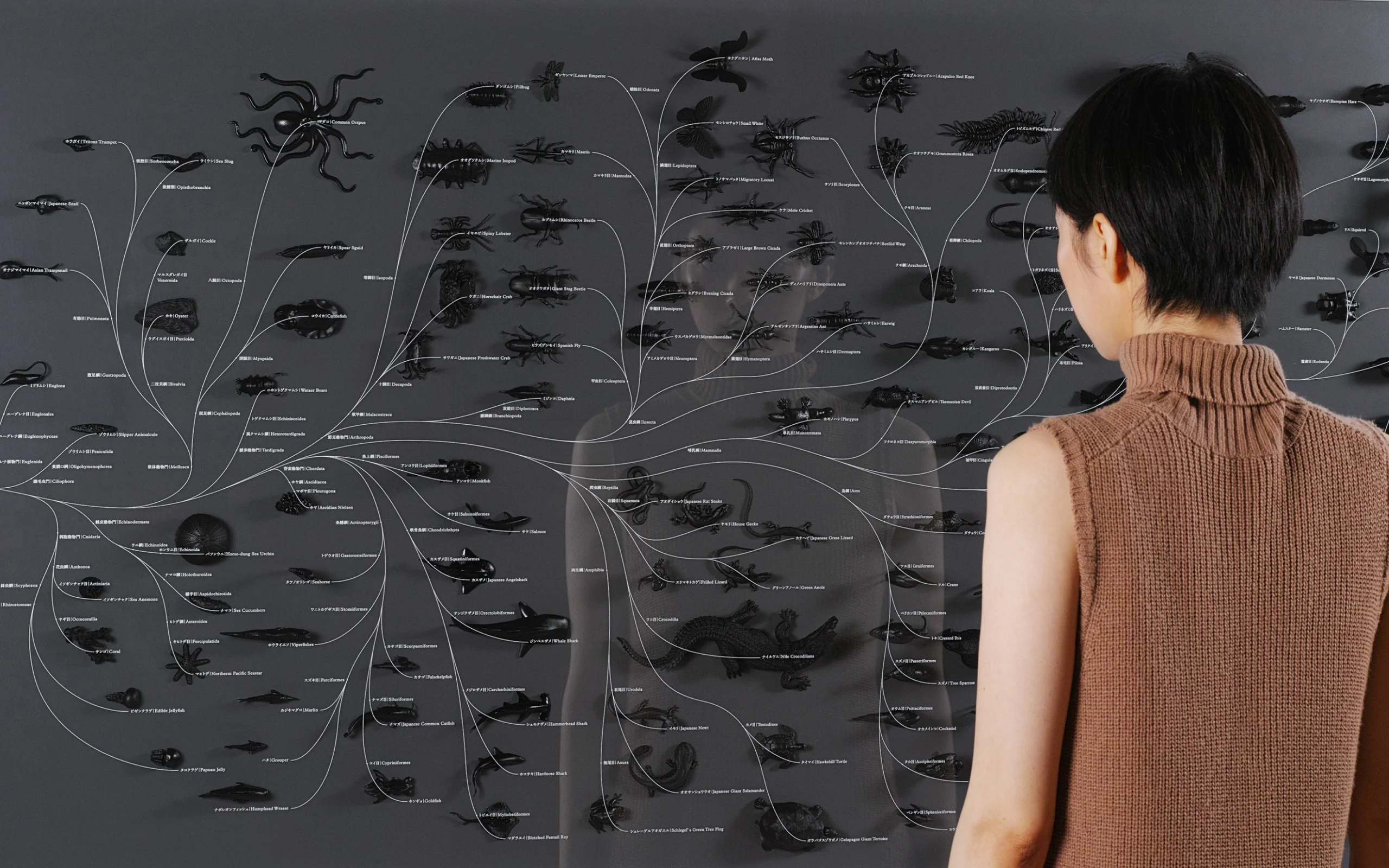
Phylogenetic tree comparing biological evolution with artificial innovation, visualizing creative gaps and innovation sources.

WHY
What is the method for reflecting on history for the future?
Society is changing drastically. Even now 50 years later since 1972, which was said to be the limit of growth for human beings, we are still growing today. Changes to halt the collapse of biodiversity and actions to keep a sustainable society no longer have a temporal grace. We need more people to change society. We often say that things “evolve” by changing society. If we say that the changing society is evolving, will we be able to learn more about then process of this evolving society, from the evolution of living things?
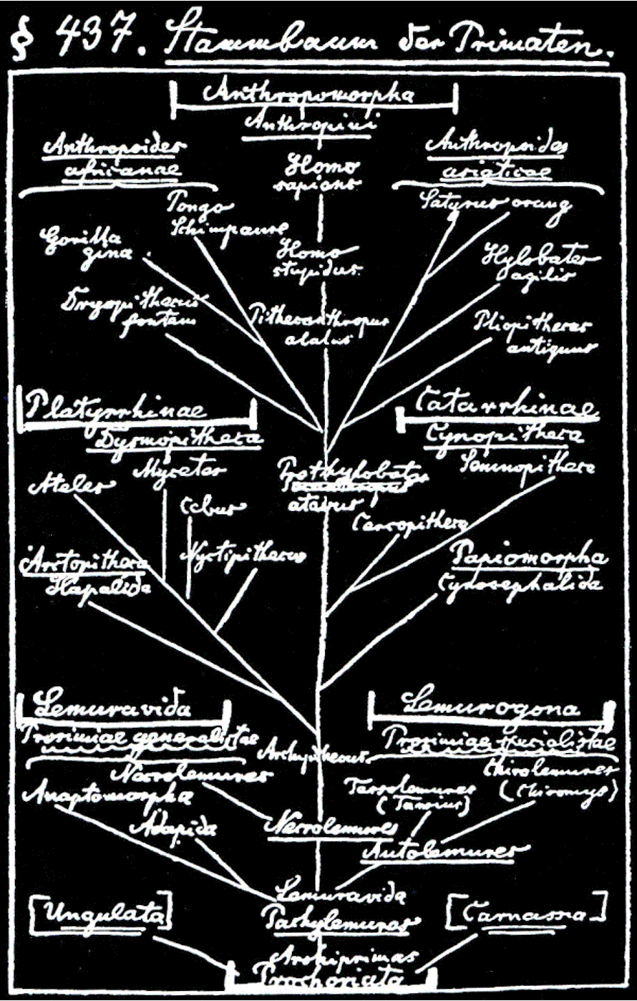
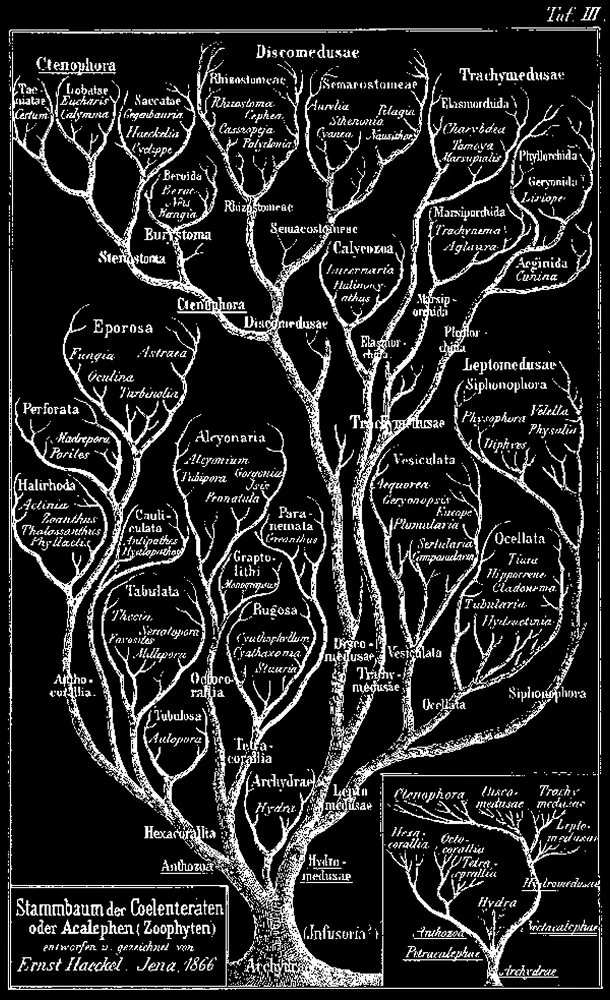
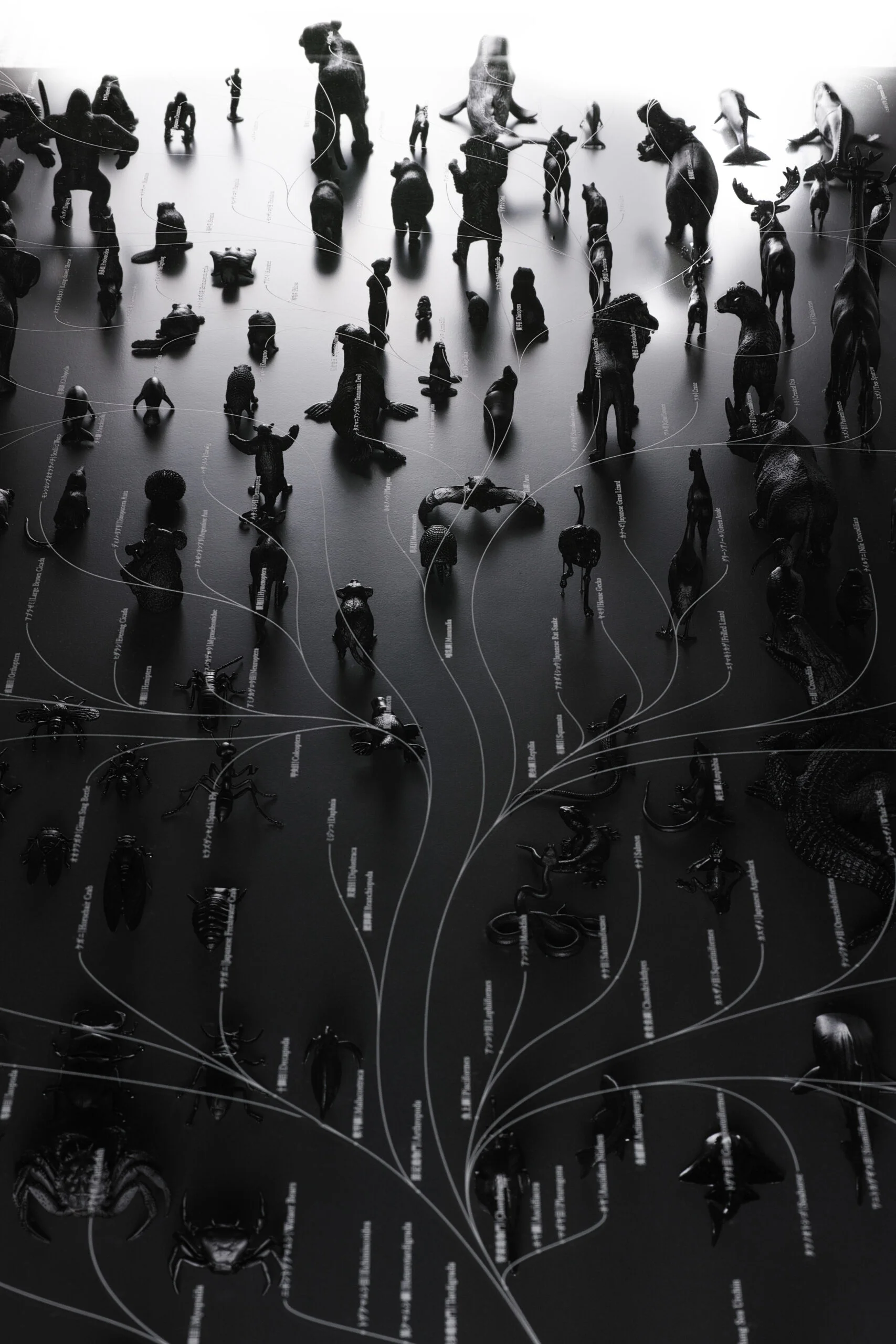
It is surprising how recently the scientific concept of evolution emerged and began to be studied systematically. For example, it was only in 1859, around 150 years ago, that Charles Darwin published Origin of Species, the work that defined the concept of evolution in a biological sense.The evolution diagram on the left is what Darwin left as a sketch. Following the thought of Darwin, Haeckel, a biologist and artist, created an expression called evolutionary tree in our image like the middle and right figure.
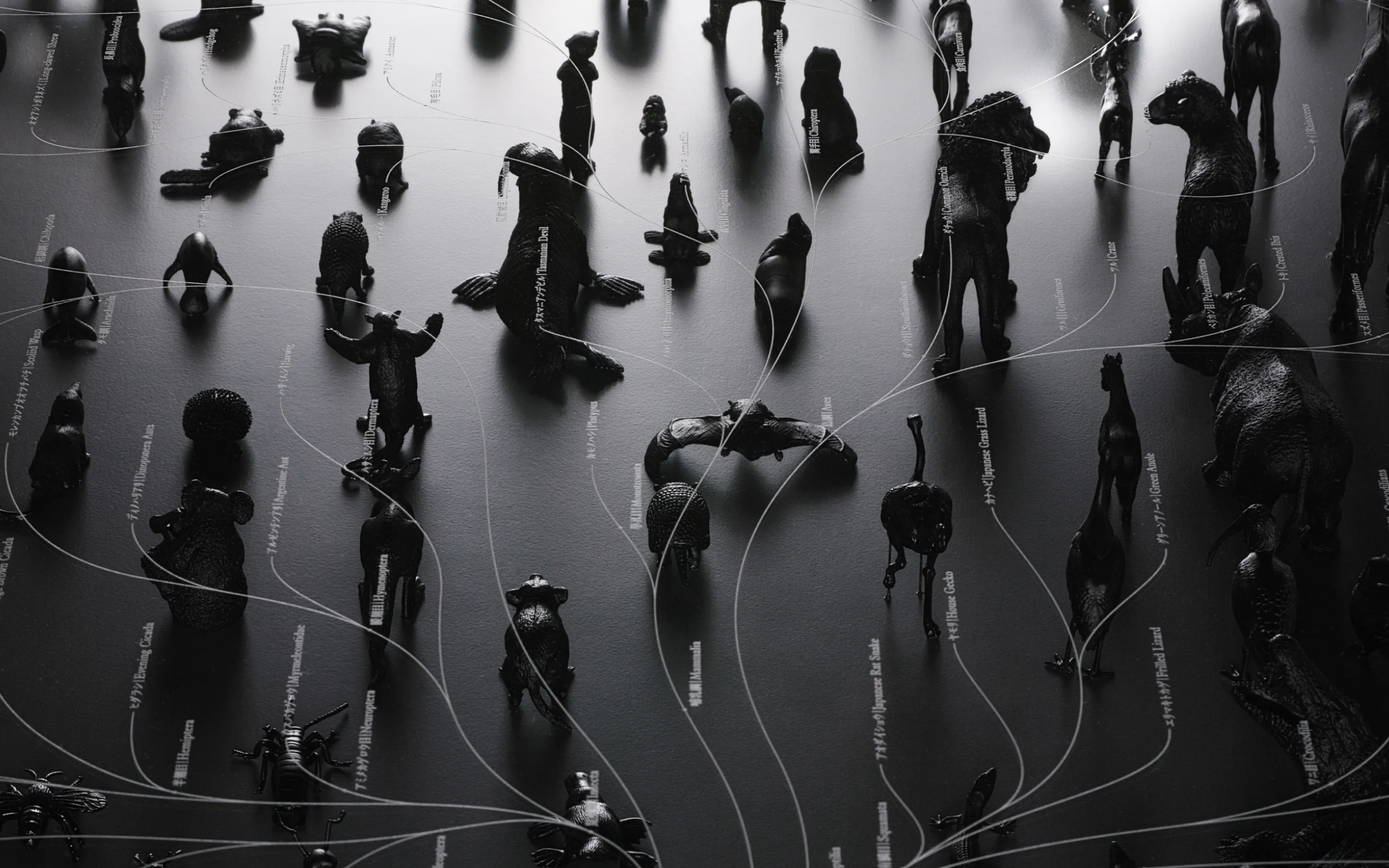
The natural world is organized in accordance with the rule of survival of the fittest, whereby species most well-adapted to the environment are the ones that survive. The natural environments changes from moment to moment, so living creatures are also in a constant state of change. The system is designed so that infinite variation is generated over time through changes in DNA, enabling a species to sustain itself no matter what the conditions. An evolutionary map is a genealogy showing those life forms that have been selected above countless others through the principle of survival of the fittest. It could equally be seen as a sketch of the survival strategy of species in the natural world.

HOW
Observe how evolutionary systems transpire, and understand the history through evolutionary diagrams.
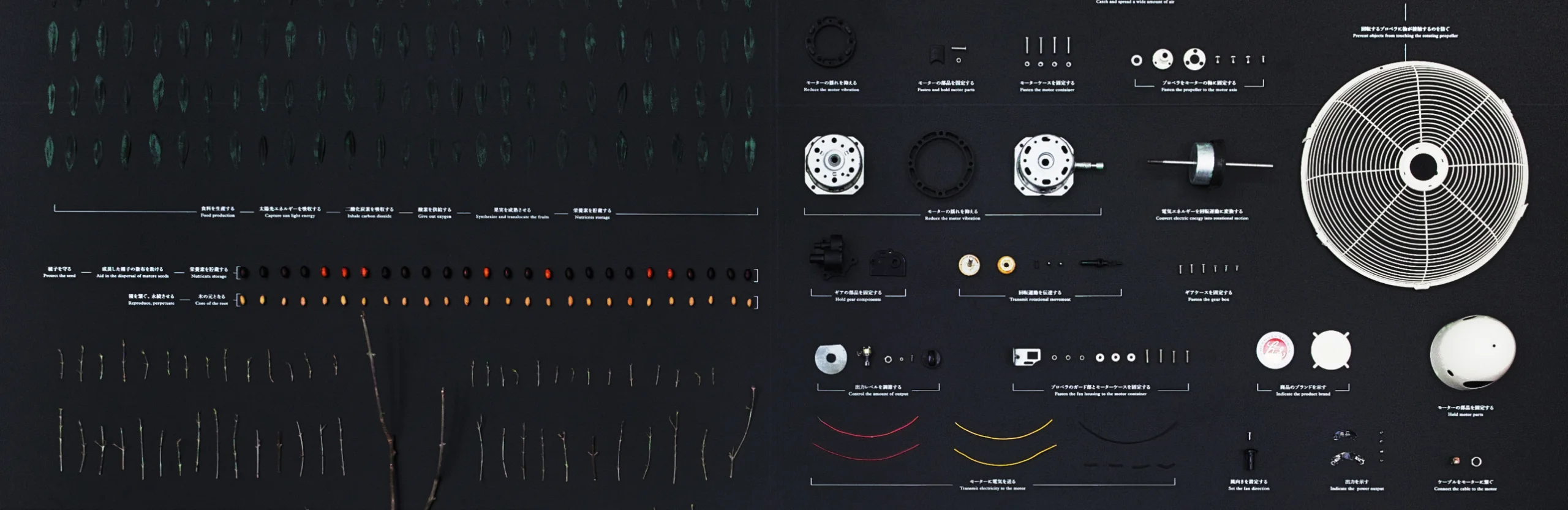
Even in the design of artifacts, things are constantly evolving and culling from advances in technology, human interests and the changing context of the times. The development of species on the premise of diversity closely resembles the form of evolution of living things. The invention constantly seeks to supplement the evolution of people. Faster, more comfortable, is not the design that has been advanced by such philosophy is the instinct of mankind who is going to evolve? If the evolution and design of living organisms are sufficiently similar, it should make it easier for innovation by understanding the process well and applying it to inventions and designs. Evolutionary thinking is a method for creative education born to learn the way of thinking from the nature.
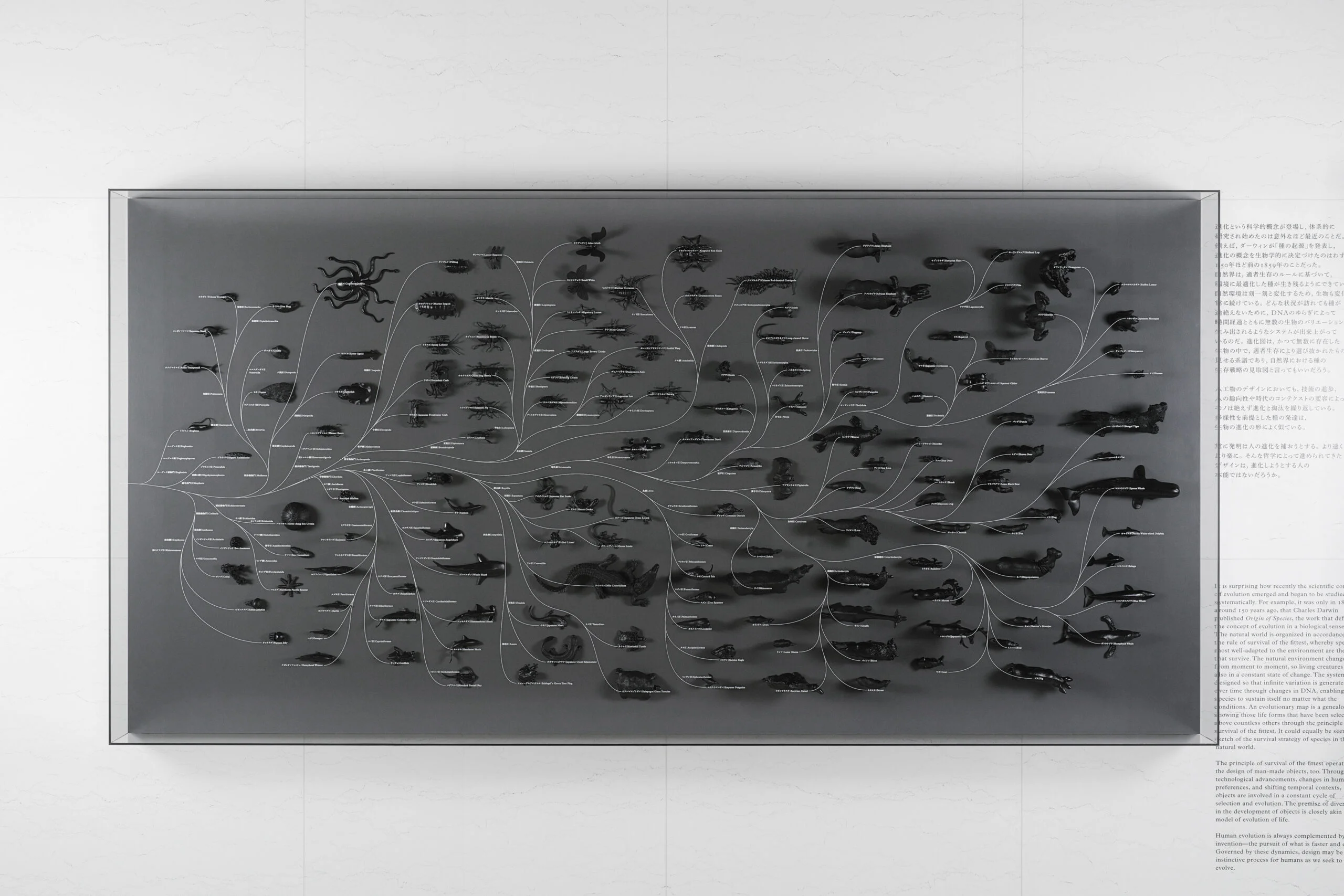


The principle of survival of the fittest operates in the design of man-made objects, too. Through technological advancements, changes in human preferences, and shifting temporal contexts, objects are involved in a constant cycle of selection and evolution. The premise of diversity in the development of objects is closely akin to the model of evolution of life. Human evolution is always completed by invention–the pursuit of what is faster and easier. Governed by these dynamics, design may be an instinctive processor humans as we seek to evolve.
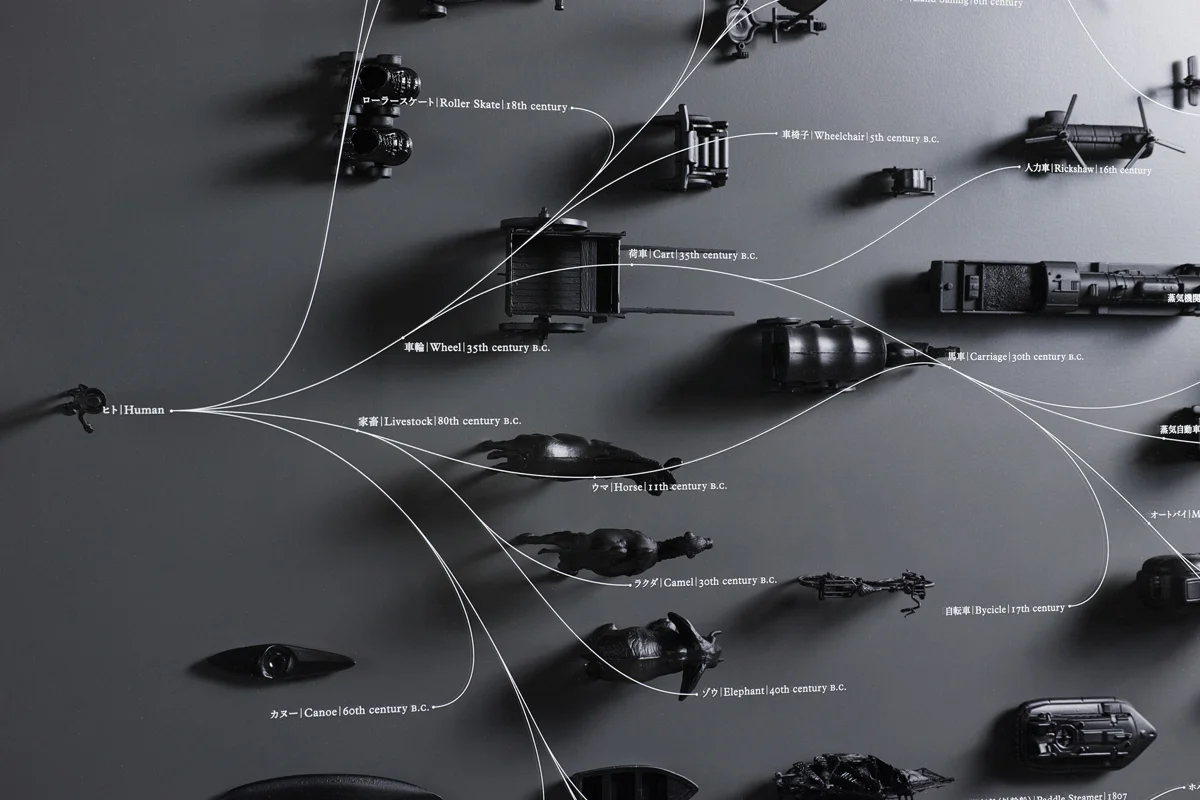
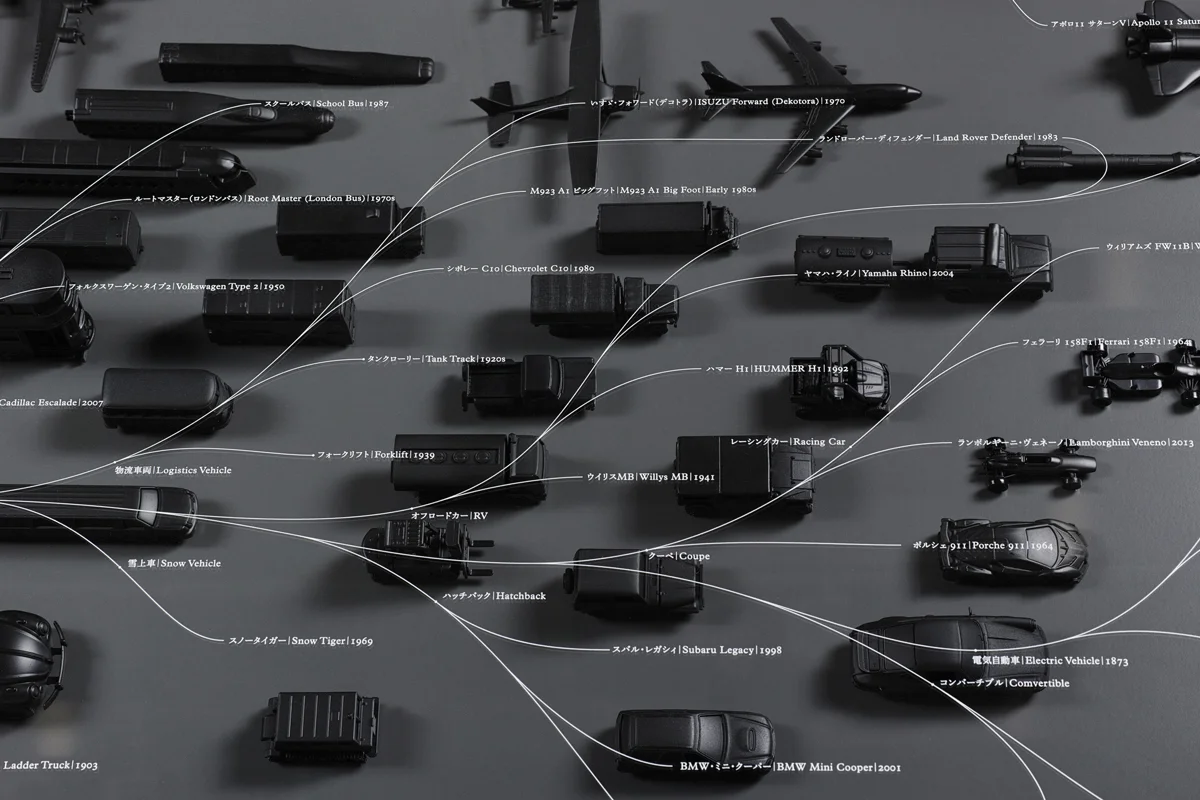
In the margins of evolutionary map of objects, there is space for objects to evolve. We may well call this space “innovation”.
We decided to draw up and compare two evolutionary maps: one of animals and one of vehicles. The anthropology of man-made objects such as vehicles is an under-developed field, and we had to begin by establishing a methodology. Then, when we reached the stage of comparing the two maps, several important differences between animals and man-made objects were revealed. For example, man-made objects are directly affected by technological advances, making the life-span of new technologies extremely short. Technology advances in a unidirectional and irreversible pattern, so the speed at which designs are selected and discarded through technological change tends to accelerate. This acceleration is why there are some outstanding 100-year-old chains that are still used today, but nobody uses mobile telephones made just 10 years ago.
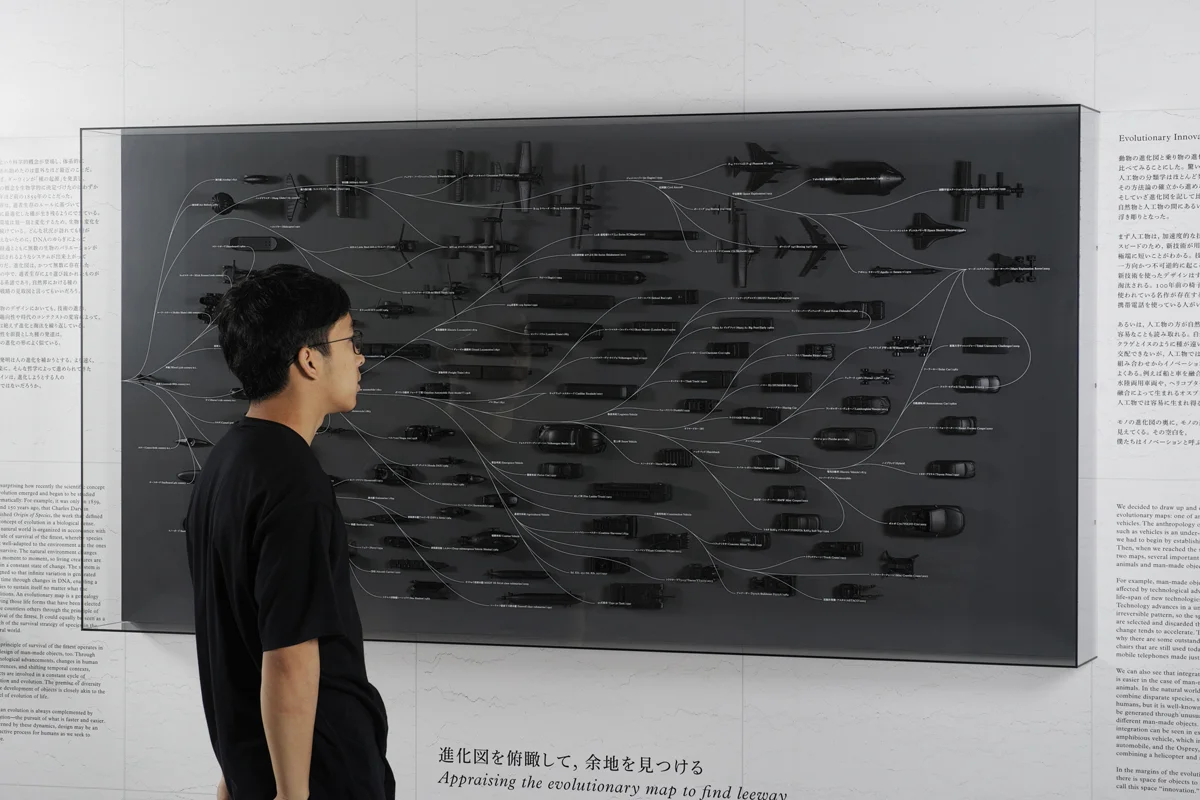

We can also see that integration of different types is easier in the case of man-made objects than animals. In the natural world, it is impossible to combine disparate species, such as jellyfish and humans, but it is well-known that innovation can be generated through unusual combinations of different man-made objects. This ease of integration can be seen in examples such as the amphibious vehicle, which integrates a boat and an automobile, and the Osprey, which was created by combining a helicopter and an airplane.

This evolutionary map was designed for “NOSIGNER–Reason behind Forms” exhibition starts from the hypothesis “What if all designs are imitations of nature, or what if the very act of designing is the act of unconsciously simulating the evolution of nature?” Through this exhibition, we compares/contrasts artificial and natural objects and explores the purpose within form, as well as ways of conceiving designs, based on the idea that “design is the biology of objects.”This philosophy became the basis of “Evolution Thinking”.
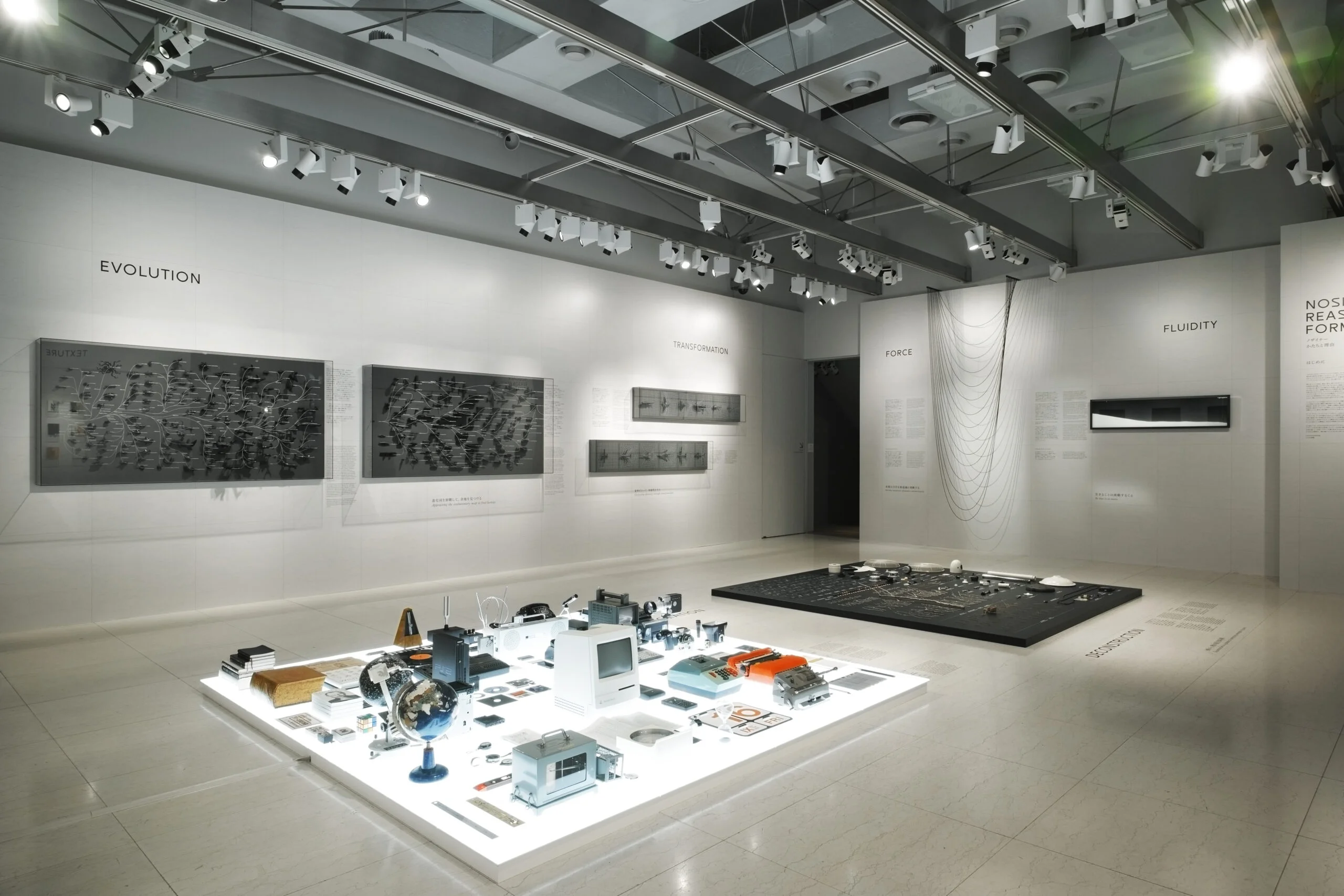

WILL
Evolutional Creativity came to be by integrating all ways of thinking.
“Evolutional Creativity” started as a small experimental exhibition, and is currently gradually spreading, while being supported by proponents such as the automobile company, the real estate company of the largest scale in Japan and the manager of the global company of apparel. (Reference article:
INFORMATION
- What
- ggg/Evolutionary Tree
- When
- 2016
- Where
- Tokyo, Japan
- Client
- Scope
- Installation / Space Design
CREDIT
- Art Work
- Eisuke Tachikawa
- Photograph
- Kunihiko Sato